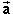 and
and  ,
, 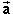 -
-  ,
is defined as the vector that added to
,
is defined as the vector that added to  gives
gives 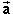 ,
,
The concept of the difference of two vectors is based on the concept of the sum of two vectors. This is analogous to how the difference of two numbers is defined.
The difference between two vectors 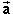 and
and  ,
, 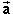 -
-  ,
is defined as the vector that added to
,
is defined as the vector that added to  gives
gives 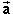 ,
,
 + (
+ (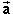 -
-  )
=
)
= 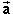 .
.
Note that algebraically this equation is an identity.
There are two methods for constructing the difference 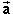 -
-  graphically.
graphically.
Comparison Method
1. Comparison Method. Arrange 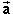 and
and  tail-to-tail, as in the diagram above, and then draw an arrow
from the tip of
tail-to-tail, as in the diagram above, and then draw an arrow
from the tip of  to the tip of
to the tip of
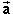 , resulting in the green vector.
The green vector is the difference
, resulting in the green vector.
The green vector is the difference 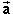 -
-  because it
satisfies the equation above. Use the tip-to-tail method of
vector addition to verify this, adding
because it
satisfies the equation above. Use the tip-to-tail method of
vector addition to verify this, adding  to
to 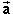 -
-  .
.
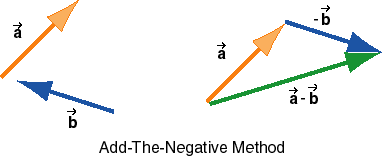
2. Add-the-Negative Method. The difference 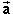 -
-  of two vectors also satisfies the equation
of two vectors also satisfies the equation
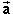 -
-  =
= 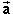 + (-
+ (- ).
).
Therefore, one can construct 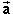 -
-  by reversing the direction of
by reversing the direction of
 to get -
to get - and then adding -
and then adding - to
to 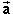 . The
preceding diagram shows the original two vectors on the left,
and the vector -
. The
preceding diagram shows the original two vectors on the left,
and the vector - added to
added to 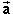 on the right.
on the right.
If one wants to calculate the difference 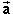 -
-  numerically,
the calculation will be based on either one of the diagrams
above. If the two vectors are given in components, their
difference is obtained simply by subtracting the components.
See Vectors/Scalar Components/Explain It, Page 14.
numerically,
the calculation will be based on either one of the diagrams
above. If the two vectors are given in components, their
difference is obtained simply by subtracting the components.
See Vectors/Scalar Components/Explain It, Page 14.