The applet will be active on Pages 2 to 5 only. On the present page, please read the following summary.
A vector is a quantity that has both magnitude and direction. Examples of vector quantities in physics are displacement, velocity, acceleration, and force.
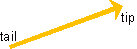
A vector can be represented graphically by an arrow:

The length of the arrow represents the magnitude of the vector.
The direction of the arrow, going from the tail end to the tip, represents the direction of the vector.