Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem
The basic work-kinetic energy theorem applies to a system
consisting of a single particle only. The general
work-kinetic energy system applies to a system of particles
that may interact with each other. A system of particles may
be gaseous, liquid, or solid. The two theorems are described
below.
Work-kinetic energy theorem for a single particle (mass
point)
If a particle is subject to a net force 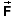 net, the
work Wnet done by the net force
on the particle during a given time interval is
equal to the change in the particle's kinetic
energy during that time interval. In symbols,
net, the
work Wnet done by the net force
on the particle during a given time interval is
equal to the change in the particle's kinetic
energy during that time interval. In symbols,
Wnet = DKE  (1)
(1)
where
KE = (m/2)v2  (2)
(2)
is the particle's kinetic energy, m the mass of the
particle and v the speed of the particle.
Work-kinetic energy theorem for a system of particles
Eq.(1) above also expresses the work-kinetic energy for a
system of particles, except that W now is the total
work done on all particles of the system and KE is the
total kinetic energy of all particles of the system.
In more detail, the total work W done on a system of
particles and the total kinetic energy KE of a system
are defined as follows. Let the system consist of N
particles, labeled 1 to N. Let us consider some time
interval during which the net force 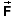 1 acting on Particle 1
does work W1 on Particle 1 and the kinetic
energy of Particle 1 changes by DKE1. Similarly for
Particles 2 to N. Then
1 acting on Particle 1
does work W1 on Particle 1 and the kinetic
energy of Particle 1 changes by DKE1. Similarly for
Particles 2 to N. Then
W = W1 + W2 + ...
+ WN  (3)
(3)
and
KE = KE1 + KE2 +
... + KEN.  (4)
(4)
To derive the work-kinetic energy theorem for a system of
particles, all one has to do is write down Eq.(1) separately
for each particle and sum the resulting N equations.
Comment. When dealing with a system of particles, one
distinguishes between internal and external forces acting on
the particles of the system. Internal forces are forces
exerted on a particle by other particles of the system, and
external forces are forces exerted on a particle by objects
that are not part of the system.
One can write the total work done on the system as the sum of
the total work done on all particles by the internal forces,
Wint, and the total work done on all
particles by the external forces, Wext,
W = Wint + Wext.
 (5)
(5)
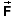 net, the
work Wnet done by the net force
on the particle during a given time interval is
equal to the change in the particle's kinetic
energy during that time interval. In symbols,
net, the
work Wnet done by the net force
on the particle during a given time interval is
equal to the change in the particle's kinetic
energy during that time interval. In symbols,
![]() (1)
(1)
![]() (2)
(2)