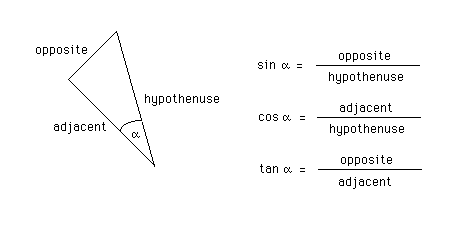
Definitions of the Sine, Cosine, Tangent, and Cotangent
The sine, cosine, tangent, and cotangent of an angle in a right-angle triangle are equal to certain ratios of the sides of the triangle. These ratios are listed for the sine, cosine, and tangent in the diagram below. The cotangent is simply the reciprocal of the tangent: cot a = 1/tan a.

Terminology
When working with a trigonometric function of an angle a in a right-angle triangle, your first step should be to find the right angle and the hypotenuse, and then the adjacent and/or the opposite to angle a .
After that, just apply the appropriate one of the equations for the sine, cosine, tangent, and cotangent listed above and make no algebraic mistakes.
On the next page you can find three examples illustrating the sine, the cosine, and the tangent.