Question (a)
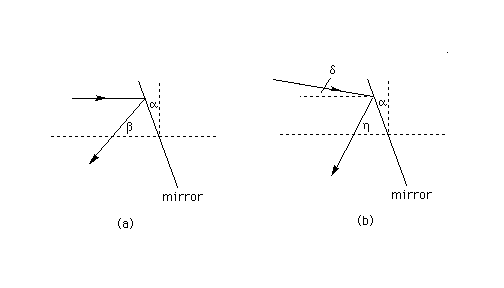
Diagram (a) below shows a plane mirror reflecting a ray of light. The diagram shows a horizontal reference axis (dashed horizontal line intersecting the mirror) and a vertical reference line (dashed). A horizontal ray of light is incident on the mirror and then reflected as shown in the diagram.

The mirror is inclined by an angle alpha relative to the vertical. Derive an expression for the angle beta between the reflected ray and the horizontal reference axis in terms of the angle alpha.
Answer.
Beta is two times alpha.
Explanation.
Diagram (a1) below shows that the angle epsilon between the normal to the mirror and the horizontal direction is equal to alpha. One can see this in two ways. (i) Angle gamma is equal to (90 deg - alpha). Since 180 deg = (epsilon + 90 deg + gamma) = (epsilon + 90 deg + (90 deg - alpha)) = 180 deg + epsilon - alpha, we find epsilon - alpha = 0, whence epsilon = alpha. (ii) The normal to the mirror and the mirror are rigidly connected by a 90-degree angle. When the mirror is vertical (i.e., alpha = 0), the normal is horizontal (i.e., epsilon = 0). When the mirror is rotated through an angle alpha, the normal rotates likewise through an angle alpha. Thus, epsilon = alpha.
Diagram (a2) shows that the reflected ray intersects two parallel lines, the incident ray and the dashed horizontal reference axis. According to a theorem from geometry, the angles formed between two parallel lines and an intersecting straight line facing each other on opposite sides of the intersecting line are equal. Therefore, beta = 2 epsilon = 2 alpha.
Question (b)
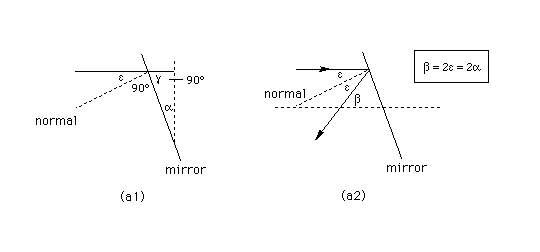
Part (b) asks the same question as Part (a) except that now the incident ray forms an angle delta with the horizontal, as illustrated in Diagram (b) above. Find an expression for the angle eta between the reflected ray and the horizontal in terms of the angles alpha and delta.
Answer.
eta = 2 alpha + delta.
Explanation.
As in Question (a), the normal to the mirror is inclined by an angle epsilon equal to alpha relative to the horizontal. Therefore, the angle of incidence is now equal to delta + epsilon. By the law of reflection, this angle is equal to the angle of reflection. If the reflected ray makes an angle equal to delta + epsilon relative to the normal and the normal makes an angle epsilon relative to the horizontal, then the reflected ray makes an angle equal to epsilon + (delta + epsilon) = delta + 2 epsilon relative to the horizontal.
By the theorem from geometry used in Part (a) above, angle eta is then equal to delta + 2 epsilon = delta + 2 alpha.